IMAGE WITH DESCRIPTION
Ra mắt sách về tinh thần đoàn kết Việt Nam và nhân dân châu Á - Phi - Mỹ Latinh
Ngân hàng ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.
VIMEO VIDEO
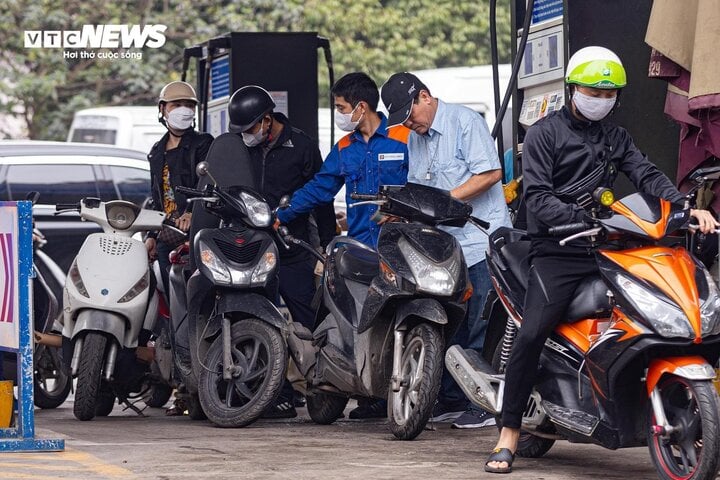
1 chỉ nhẫn vàng 9999 giá bao nhiêu?
Kinh doanh ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.
HTML5 MUSIC W/ FLASH FALLBACK
Quân đội Israel tuyên bố 'tạm dừng chiến thuật' ở Gaza để tiếp tế viện trợ8KBET
Làm tóc ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.
YOUTUBE VIDEO
Vụ 3 thanh niên chết trên đường Láng: Tạm giữ 25 người8KBET
Điện thoại di động ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.
LOAD A FLASH FILE
8KBETĂn nhầm bả chó, bé 22 tháng tuổi nguy kịch
Startup ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.
Vì sao bạn nên ăn một quả táo mỗi ngày?-8KBET - link mới
8KBETThời tiết ngày 20/6: Nắng nóng bao trùm Bắc-Trung Bộ, chiều tối có thể mưa dông, tincidunt sed quam. Duis dignissim nunc et diam volutpat et ultrices nulla venenatis. Etiam eu augue eu nibh lobortis pretium eu non velit. Curabitur erat arcu, consequat sit amet hendrerit eget, mollis quis erat. Nullam turpis metus, dictum ac porta ut, volutpat et lectus. Nunc et enim metus, sed sagittis nulla. Fusce sed augue id enim condimentum lacinia ac quis dui. Praesent nibh purus, convallis a congue at, facilisis in massas

IMAGE WITH DESCRIPTION
Belarus trở thành thành viên thứ 10 của SCO-Đăng Ký Đại Lý Tại 8KBET win
Tin tức chính ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.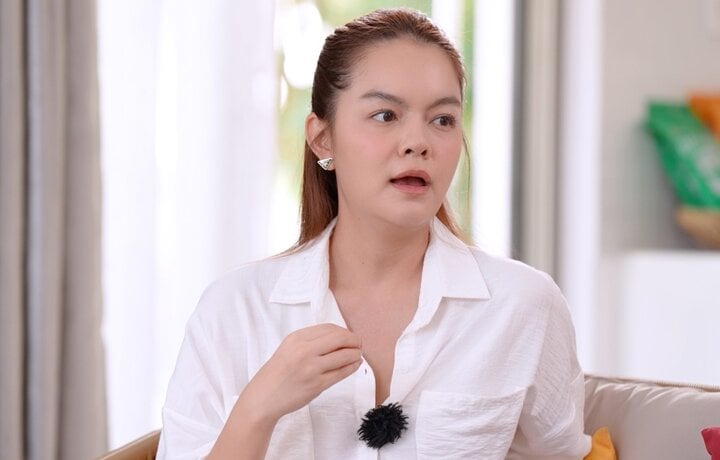
IMAGE WITH DESCRIPTION
Ông Zelensky phác thảo mô hình đàm phán với Nga-8KBET hướng dẫn nạp tiền Viettel Pay
Education ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.
IMAGE WITH DESCRIPTION
Những sai lầm khi sử dụng xe máy điện vào mùa mưa-8KBET bắn cá casino có uy tín không
Thủ công mỹ nghệ ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.
IMAGE WITH DESCRIPTION
Đắk Lắk thanh tra vụ hơn 7.300ha rừng tự nhiên bị suy giảm-Dịch Vụ Điều Hướng 8KBET
Đổi mới ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.
IMAGE WITH DESCRIPTION
Dự báo thời tiết TP.HCM ngày 30/6: Nắng nóng, chỉ số tia UV cao-8KBET tải bắn cá long vương
Lâm nghiệp ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.
IMAGE WITH DESCRIPTION
Chỉ số Nasdaq lập kỷ lục mới-vào lại website 8KBETb
Tài sản ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.
IMAGE WITH DESCRIPTION
Big4 ở Việt Nam là những ngân hàng nào?-8KBET doanh thu ngày
Sáng tạo ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.
IMAGE WITH DESCRIPTION
Xác thực sinh trắc học bị 'lừa' bởi ảnh tĩnh: Chuyên gia nói không phải là lỗi-8KBET win
Sống khỏe đẹp ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.
IMAGE WITH DESCRIPTION
Học vấn đáng nể của Á hậu cuộc thi Mrs Earth Vietnam 2024 Lê Thị Mai-8KBET bảo trì đến bao giờ
Bơi lội ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.
IMAGE WITH DESCRIPTION
Dự báo thời tiết tuần tới: Miền Bắc hứng mưa to, chấm dứt nắng nóng-kinh nghiệm rút tiền 8KBET
Sáng tạo ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.
IMAGE WITH DESCRIPTION
Thắng Sơn La, TP.HCM I tiếp tục dẫn đầu giải nữ VĐQG 2024-baccarat 8KBET online
Chính trị ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.
IMAGE WITH DESCRIPTION
Nghe vô lý nhưng lại rất thuyết phục: Apple đưa camera lên Airpods-đánh giá 8KBET
live ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.
IMAGE WITH DESCRIPTION
Trạm cứu hộ trái tim tập 41: Ngân Hà bị An Nhiên tát, bị mẹ Vũ sỉ nhục
Móng tay móng chân ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In est metus, tincidunt vitae eleifend sit amet, porta a sapien. Fusce in dolor nec purus facilisis dictum. tincidunt sed quam.CLB Manchester Utd thông báo đã đạt được thỏa thuận gia hạn hợp đồng thêm một năm với HLV Erik ten Hag.-8KBET sàn cá cược

